|
our cosmos is life's creation |
|
|
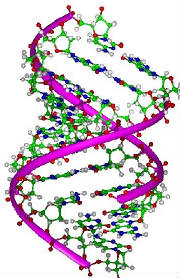
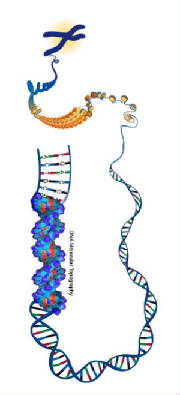
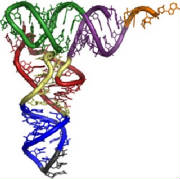
33 - DNA double helix molecule.
Fortunately this world can be controlled by Robots, created for this
purpose to eliminate human error. They make what we Create in our Imagination, find reflection in the real world that
we can see as IDREA. We are making the Cosmos of Life's Creation. Yes - in the hands of those who know how, an Artezan. The
Aura of Technology - We trust them, but wish they all make the sacred oath to LIFE
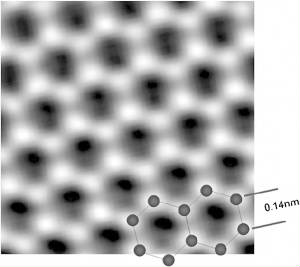
- just to be sure things turn out right, in our favor. Graphene is a sheet of carbon atoms one atom thick, the distance between
two atoms is 0.14nm - the history of each photon is the history of Vision engraved in the memory of All.
Only a very elementary outline can be presented here. There is a remarkable similarity between the DNA molecule and a computer
program. The foundations of modern computer science were laid down by Janos von Neumann (1903–1957) Unlike computer binary systems, the DNA molecule uses four basic units for storing information which are often shown
in illustrations as the four aces of a deck of playing cards. Four types of data are essential to the working of the molecule. The four bases or nucleotides are as follows: A adenine Pairs with thymine in DNA or uracil in RNA T thymine Pairs with adenine. C cytosine recently found use in quantum computation. the classical bit —with additional dimensions associated to the quantum properties of a physical atom. The first time any quantum mechanical properties were harnessed to process information took place on August 1st in 1998 when researchers at Oxford implemented David Deutsch's algorithm on a two qubit NMRQC (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Quantum Computer) based on the cytosine molecule. This molecule has found a place in Molecular Computing. G guanine – in concentration from guano: sea-fowl excrement.Guanine is used as an additive to cosmetics and
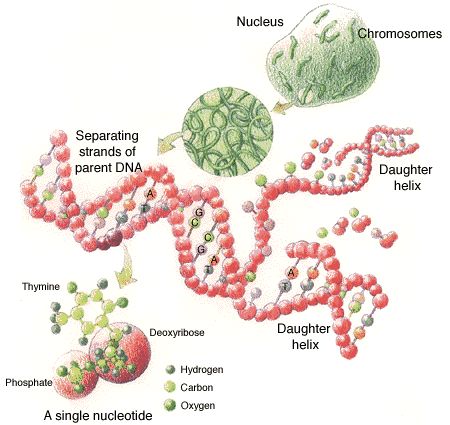
shampoo to give a pearly lustre. The nucleotides bond together in four ways to make the rungs of the ladder: A+T, T+A, C+G and G+C, so that both sides of the ladder will have all four nucleotides. The backbones of the ladder consist of alternate sugar (deoxyribose) and phosphate molecules. The nucleotides bond to the sugar molecules. It is the sequence of the four types of ladder rungs that make up the program of the molecule in much the same way as ones and zeroes make up a computer program. The DNA molecule is in effect a Turing machine. The basic grouping of the base pairs is in groups of three called codons. The codon corresponds to a byte in computermemory. The three pair codon provides sixty four possible values. Some codons (UAA, UGA and UAG) act as delimiters and serve no other purpose. This corresponds to the NOP (no-operation) instruction of a computer program. When referring to a codon as UGA this implies the base pairs U+A, G+C and A+T but it is sufficient to mention only one side of the ladder.
The genome occupies only about five centimetres of the molecule – no purpose for the rest of the molecule has been discovered. This is not to say that it is not very useful. This is the part that is used by forensic scientists for DNA fingerprinting. This is most useful for identifying criminals and settling paternity disputes. The DNA molecule would not survive very well as a long thread but is fortunately very compactly coiled up around spoollike proteins in chromosomes known as histones.
Despite its extreme complexity, DNA has a remarkable ability for survival. DNA has actually been extracted from 30 000 year old ground sloth dung and it has even been suggested that DNA can be extracted from million year old samples! Studies of DNA taken from the extinct Mauritian Dodo have showed that it is related to the common pigeon. DNA has also been extracted from a quick-frozen ice age woolly mammoth. A most significant result of a DNA study was announced in 1997 which confirmed that the Neanderthals were a distinct species which had become extinct and did not contribute to the DNA of modern humans.
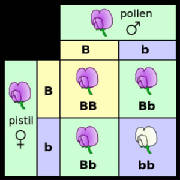
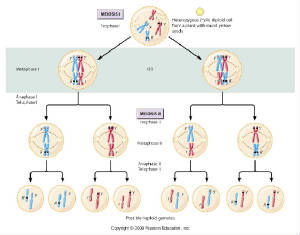
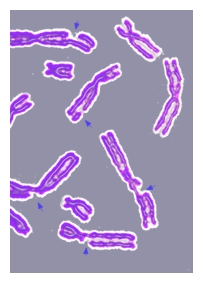
All plants and animals have chromosomes which form part of the cell nucleus of living tissue. The chromosomes in turn contains a vast number of genes along its length which define protein production. The name chromosome (coloured body) is a misnomer – an object of this size is much smaller than light wavelengths and cannot therefore have colour, but they can be microscopically observed if heavily stained. From the table given here, it will be seen that the number of chromosomes bears little relation to the size or complexity of the organism.
The XX and XY arrangement ensures that there will be an equal chance of male or female offspring being produced. In humans, the males and females are physically quite different from head to toe, as well as mentally and emotionally, yet the only genetic difference is in one out of forty six chromosomes.
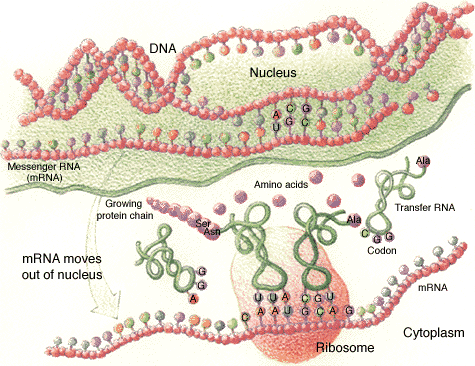
The DNA molecule is not
directly involved in the expression of genes. The genes are transcribed into a second type of nucleic acid, RNA (Ribonucleic
acid) which is typically single stranded and with the sugar ribose instead of deoxyribose. This molecule is much less
stable than DNA. Not all parts of a gene are used for encoding products. Regions called introns are removed from the messenger
RNA in a process called splicing and regions encoding products are called exons. A
significant portion of gene coding is devoted to controlling and switching off protein production. This is somewhat similar
to computer data transmission where a significant portion of the data stream exercises controlling, handshaking and data integrity
functions. This is curiously referred to as ‘line protocol’. The control aspect of genes
is obviously necessary – genes responsible for the growth of an ear should not produce fingers, toes or eyes
like a Picasso painting. The self-repair aspect of DNA is astonishing to the point of miraculous. It has been estimated that the DNA in a single cell can be damaged up to 10 000 times a day by carcinogens and radiation. The DNA can even be damaged by products within the cell. The DNA molecule will take this damage in its stride but occasionally the damage will remain unattended resulting in the start of mutation or cancerous growth.
Esters are chemical compounds derived by reacting an oxoacid (one containing an oxo group, X=O) with a hydroxyl compound such as an alcohol or phenol. Esters are usually derived from an inorganic acid or organic acid in which at least one -OH (hydroxyl) group is replaced by an -O-alkyl (alkoxy) group, and most commonly from carboxylic acids and alcohols. Basically, esters are formed by condensing an acid with an alcohol.Esters are ubiquitous. Many naturally occurring fats and oils are the fatty acid esters of glycerol. Esters with low molecular weight are commonly used as fragrances and found in essential oils and pheromones. Phosphoesters form the backbone of DNA molecules. Nitrate esters, such as nitroglycerin, are known for their explosive properties, while polyesters are important plastics, with monomers linked by ester moieties.
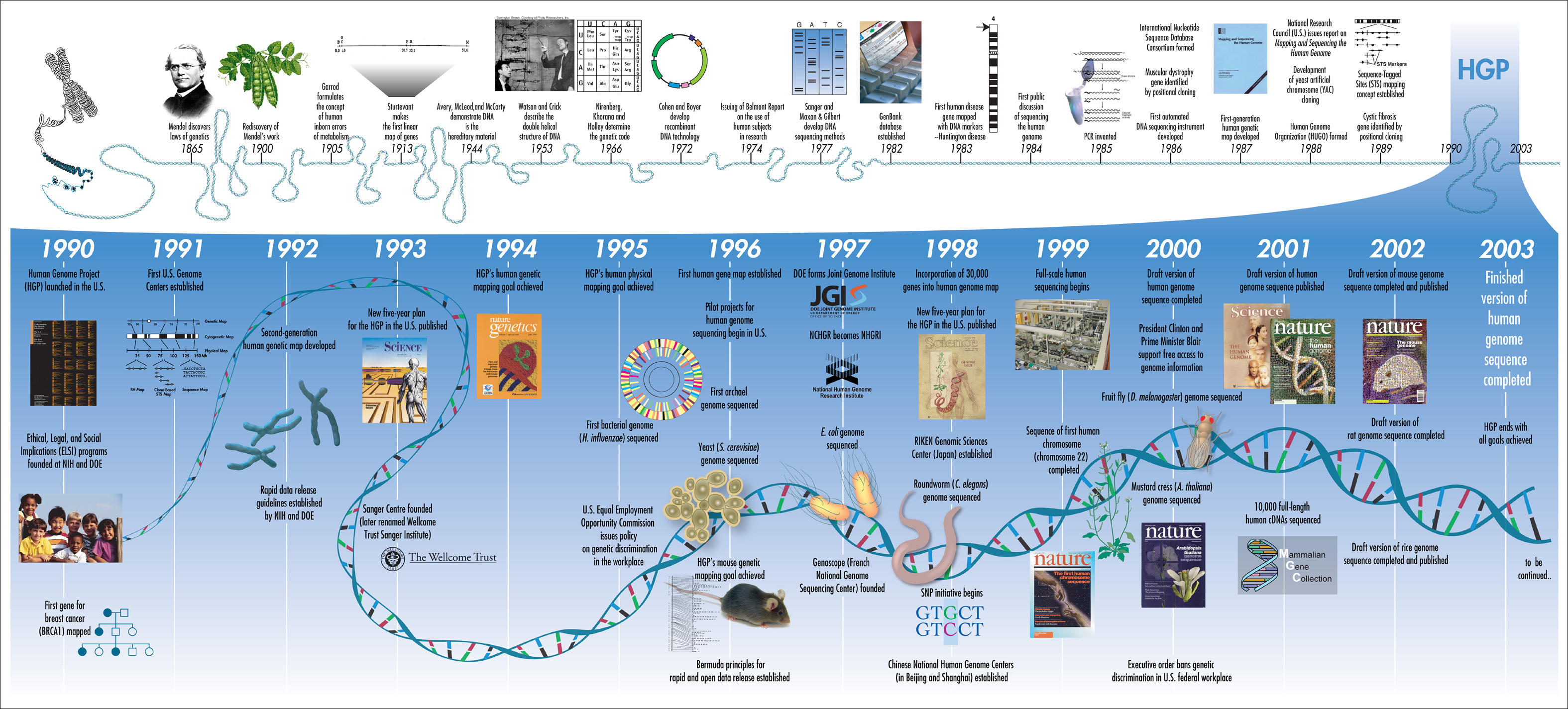
The project was completed ahead of schedule in 2003 making a vast wealth of information available
for further research. There is of course no single human genome – each individual has a genome slightly different to
that of everyone else.
For each successive human generation the offspring will have a new DNA configuration. In addition
to the DNA molecules that make up the chromosomes within the cell nuclei, the cells also have many organelles called mitochondria
which contain circular DNA loops called mitochondrial DNA. The mitochondrial DNA does not express traits and does not change
from one generation to the next unless mutations occur. Mitochondrial DNA is contained in ova but not in sperm so that this
DNA can only be transmitted to the next generation by the female parent. Mitochondria therefore provide a useful means of
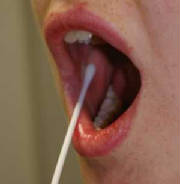
tracing female ancestry back for as many generations as DNA can be found. A remarkable project was launched in 2005 to study historical human migration patterns by analyzing DNA samples from hundreds of thousands of people from all parts of the world. This is a privately funded collaboration between IBM, the National Geographic Society and the Waitt Family Foundation. This huge anthropology project is expected to run for five years. The samples are taken by means of mouth swabs (buccal swabs). The project also includes the sale of selftesting kits which can be purchased through the post. People purchasing the kits can have the migration of their early ancestors determined either by mitochondrial DNA or chromosome-Y DNA. The mitochondrial DNA trace will give results for female ancestry and the chromosome Y test will show male ancestry. Women wishing to trace their male ancestry must obtain the swab from a close male family member. Profits from the sale of kits are ploughed into a Legacy Fund which will be spent on cultural preservation projects. This exciting project has already produced fascinating results but sadly it has also met with opposition from people who feel their tribal identity under threat.
Another remarkable possibility is the use of molecules for data storage. Information stored in DNA-like molecules would mean that millions of digitised photographs could be stored in a piece of material scarcely large enough to be visible. Finding a workable storage and retrieval method to access this data is a matter still in the realm of science fiction.This is where I am now. To find a way to unload al this images of Frozen moments in time.
The human
genome contains 3.2 billion chemical nucleotide
base pairs (A, C, T, and
G). · The average gene consists
of 3,000 base pairs, but sizes vary greatly, with the largest known human gene
being dystrophin at 2.4 million base pairs. Functions are unknown for more than 50% of discovered genes. The human genome sequence is almost exactly
the same (99.9%) in all people. ·
About 2% of the genome encodes instructions for the synthesis of proteins. ·
Repeat sequences that do not code for proteins make up at least 50%
of the human genome. ·
Repeat sequences are thought to have no direct functions, but they
shed light on chromosome structure and dynamics. Over time, these repeats reshape the genome by rearranging it, thereby creating
entirely new genes or modifying and reshuffling existing genes. · The human genome has a much greater portion (50%) of repeat sequences than the mustard
weed (11 %), the worm (7%), and the fly (3%). · Over 40°/o of predicted human proteins share similarity
with fruit-fly or worm proteins. · chromosome 1 (the largest
human chromosome) has the most genes (3,168), and Y chromosome has the
fewest (344). · Particular gene sequences have been associated
with numerous diseases and disorders, including breast cancer, muscle disease,
deafness, and blindness. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Click on the buttons below for other pages . . .
|