|
our cosmos is life's creation |
|
|
71 - Worlds of the micro y macro cosm
Life is that what recombined, re-created, changed all the elements of
the Universe (Byronic Matter) at atomic scale atom by atom - into double helix living structures. Called
the replication of the DNA molecule - “The
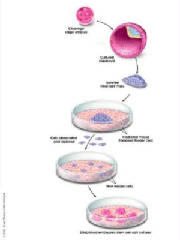
very first thing that embryonic stem cells do, without any effort at all, is that they make neurons,” our cell
make up reflect the presence of multiple organisms working together in harmony a human cell contain up to 1500 mitochondria energy sources from microbial origins - Bio-Logica .
it is also good to know every spermatozoon DNA double helix molecule is impulsed by one of these, with a tail to steer on a pheromone trail following a calling sign from a beacon in space . A dark force is that power, that brings matter under control - the dark controlling force - is a life force - as life is a form of intelligent energy - created out of the matter of the Universe - We are all children of light and star dust - As all we eat comes from the sun - all the biomass we consume derive its assembly and energies from Inti. Also good to know that the red color of our blood is from iron atoms, formed in super nova stellar explosions but now, intelligence can exist without this Sun-God-Inti or call him Aten if you wish Man have entered the era of light, insight and vision, to see and make his future very
clear
“Reality
isn't a thing or static place,” “It’s a Biological process.” Bio-Logica. The very first
thing embryonic mother cells do, without any effort at all "Wu Wei" they make neurons for communication “They are
assembling basically the building blocks of reality. If you look at embryonic stem cells, or the Ants they can do everything - just
like us, every
cell of the body is inter connected to communicate with what we call neurons, pheromones, just like words - it is about the right vibration, intonation and sequence of command As we do on the
Internet - Now I am talking to you.
The laws of physics and chemistry can explain the biology of living systems, in detail. Right down to the chemical foundations and cellular organization of Bio-Cells, it is all about Bio-Logica: oxidation, biophysical metabolism, the carbohydrates and amino acid patterns. Every living creature is the center of his own Aura and reality. In fact, space and time fall into the realm of Bio-Reason as animal sense perception - not of physics. They are properties of the mind, Consciousness cannot exist without a living creature Life embody its perceptive powers of creation. Therefore we must turn to the logica of Life, to Bio-Logica, if we are to understand the world around us. Is to see the reflected light from the living
The Macrocosm mirror the Microcosm The spinning atoms in Hafnium Carbide Crystals "lock in resonance together" in the same stable geometric shape as the face of the crystals. I think the word is to resonate in harmony. The light of knowledge, enlighten the dark matter. See the magic world of the Living. All
Life with the Double Helix structure is the sacred creator of all. .
Must be under control
and directed to our advantage. Intelligent Objective Reason must Re-Create the whole order of the Universe by Bio-Logica Synchronize movement to create order in harmony. Like cosmic music - echo in our IDREA.
Intelligent Reason is the Logica to
indicate where everything should go. Intelligence
is seated here on mother earth from where it will expand into alternative life forms of our making. To explore the Universe as if with our own eyes - looking deeper into visual time, under our control. Light is life's energy and reflected light
a visual source for memory Intelligence is know how to interpret all detail in that visual world. Have insight into the whole story
which is the scope and extend of all reflected light. We are children of light it is the essence of everything we eat entwined in the DNA
of our genetic make-up. Reflected light spin energy
is the content of this memory. It is all about
vision - connected at the speed of thought.
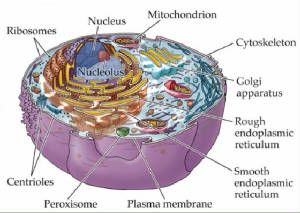
The constellation of all proteins in a cell
is called its proteome. Unlike the relatively unchanging genome, the dynamic proteome changes from minute to minute in response to tens of thousands of intra -and extracellular environmental
signals.
A protein's chemistry and behavior are determined by the gene sequence and by the number and identities of other proteins made in the same cell at the same time and with which it associates and reacts. Studies to explore protein structure and activities, known as proteomics, will be the focus of much research for decades to come and will elucidate the nutrient-sensing systems, molecular basis of health and disease.
Nanotechnology is very diverse, ranging from extensions of conventional device physics to completely new approaches based upon molecular self-assembly, from developing new materials with dimensions on the nanoscale to direct control of matter on the atomic scale. Nanotechnology entails the application of fields of science as diverse as surface science, organic chemistry, molecular biology, semiconductor physics, microfabrication, etc.
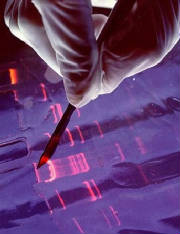
 The DNA in each human cell is packaged into
46 chromosomes arranged
into 23 pairs. Each chromosome is a physically separate molecule of DNA that ranges in length from about 50 million to 250 million base pairs. A few types of major chromosomal abnormalities, including
missing or extra copies or gross breaks and rejoining (translocations), can be detected by microscopic examination. Most changes in DNA, however, are more subtle and require a closer analysis of the DNA
molecule to find perhaps single-base differences.
Enter content here |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Click on the buttons below for other pages . . .
|